Solar Eclipse: Witness the Awe-Inspiring Power of a Sun Blackout
More Research from NASA’s Solar Eclipse
NASA’s Solar Eclipse Website: Introduce NASA’s dedicated website on solar eclipses, which provides a wealth of information for the public and researchers alike.
NASA’s Eclipse Missions: Highlight NASA’s ongoing missions dedicated to studying the sun and its corona, particularly during solar eclipses. You can mention specific missions like.
The Coronal Temperature Mapper (Hi-CAT): This instrument flew on a suborbital rocket during the 2017 total solar eclipse to measure the temperature of the sun’s corona with unprecedented detail.
Introduction
Begin with a captivating description of a total eclipse, highlighting the sudden descent into darkness and the awe-inspiring sight of the sun’s corona.
The Power of the Sun: Briefly discuss the sun as our solar system’s central star, its immense power source, and its role in sustaining life on Earth.
Sun Blackout – A Celestial Event: Introduce the concept of a eclipse, emphasizing the temporary alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth that causes the sun’s apparent blackout.
A Rare Spectacle: Explain the relatively infrequent occurrence of total solar eclipses due to the specific alignment requirements. Mention the worldwide fascination and scientific importance of these events.
Types of Sun Blackout
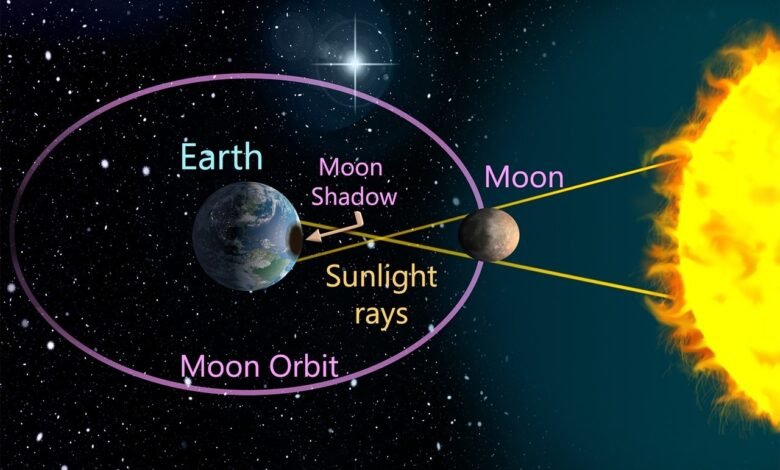
Total Solar Eclipse: Provide a detailed explanation of a total eclipse, where the moon completely covers the sun’s bright face, revealing the faint corona. Discuss the concept of the umbra (complete shadow) and penumbra (partial shadow) cast by the moon during the eclipse.
Partial Solar Eclipse: Describe a partial solar eclipse, where the moon only covers a portion of the sun’s disc, leaving a crescent or ring of sunlight visible. Explain the varying degrees of visibility depending on the observer’s location.
Annular Solar Eclipse: Introduce the concept of an annular eclipse, where the moon appears smaller than the sun and casts a dark core (umbra) surrounded by a bright ring of sunlight (corona).
Witnessing a Total Solar Eclipse
Safety First: Stress the absolute importance of using properly filtered solar glasses or eclipse viewers to observe a solar eclipse directly. Looking directly at the sun, even during an eclipse, can cause permanent eye damage.
Phases of a Total Eclipse: Describe the different phases of a total eclipse:
Partial Eclipse The moon begins to obscure the sun’s disc, creating a crescent shape.
Totality: The moon completely covers the sun, plunging the day into twilight for a brief period (typically a few minutes). During totality, the breathtaking corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere, becomes visible.
Partial Eclipse Resumes: The moon begins to move away from the sun, and the sun’s disc becomes progressively visible again.
Awe-Inspiring Observations: Discuss the unique visual phenomena observable during totality, such as Baily’s beads (sunlight shining through valleys on the moon’s edge) and solar prominences (gaseous eruptions from the sun’s surface). Mention the sudden drop in temperature and the appearance of stars and planets during totality.
The Science Behind Sun Blackout
Celestial Mechanics: Explain the astronomical principles behind solar eclipses. Discuss the moon’s orbit around Earth and the tilted plane of the moon’s ecliptic relative to Earth’s ecliptic. How these alignments create the conditions for eclipses.
Path of Totality: Describe the path of totality, a narrow band on Earth’s surface where a total solar eclipse is visible. Explain how the moon’s shadow sweeps across the Earth during the eclipse.
Predicting Eclipses: Highlight the ability of astronomers to predict eclipses with great accuracy. Discuss the use of historical records and sophisticated astronomical calculations to forecast future eclipses.
The Importance of Studying Blackout
Solar Corona: Explain how eclipses provide astronomers with a unique opportunity to study the sun’s faint corona, which is normally obscured by the sun’s bright face.
Solar Activity: Discuss how observations of the corona during eclipses can help us understand solar activity, including solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can impact Earth’s technology and climate.
Testing Theories: Mention how eclipses can be used to test theories about general relativity, as the sun’s immense gravity bends light from background stars, observable during totality.
Future of Solar Research: Briefly discuss how ongoing and future eclipse observations contribute to our understanding of the sun and its impact on our solar system.
Read More: Familiar Decays Sifting Through the Known: ATLAS Search for New in Familiar Decays
More Research from NASA
The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST): This state-of-the-art telescope, currently under construction, will be able to observe the sun’s corona in much greater detail than ever before, even without the aid of a solar eclipse.
Citizen Science Opportunities: Discuss how NASA incorporates citizen science initiatives related to solar eclipses. This could involve tasks like collecting data on sky brightness changes during totality or participating in image analysis projects.
The Future of Eclipse Research: Conclude this section by mentioning NASA’s continued commitment to studying eclipses and the sun’s impact on Earth. Briefly touch upon future missions and scientific goals related to solar research.
Cultural Significance of Eclipse
Historical References: Provide examples of how solar eclipses have been documented and interpreted throughout history by various cultures. Discuss the myths and legends associated with these events.
Modern-Day Fascination: Highlight the continued global fascination with eclipses, drawing large crowds of eclipse chasers and inspiring awe and wonder.
Educational Opportunities: Mention the educational value of solar eclipses, sparking scientific curiosity and promoting public engagement with astronomy.
Conclusion
Recap the Awe-Inspiring Power: Briefly summarize the captivating nature of eclipses and the unique opportunity they provide to witness the sun’s power and the intricate workings of our solar system.
Importance of Scientific Study: Reiterate the importance of studying solar eclipses for scientific advancement, including understanding the sun’s influence on Earth and testing fundamental theories.
Looking to the Future: Conclude with a hopeful outlook on the future of solar research, with NASA playing a leading role in unraveling the mysteries of our sun and its impact on our universe.
Here’s the continuation of the outline, incorporating NASA’s research and upcoming missions.




Hi,
Defiantly…